Plastic Polymer Chemistry . plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. define key terms used in polymer chemistry. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful.
from www.alamy.com
plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. define key terms used in polymer chemistry.
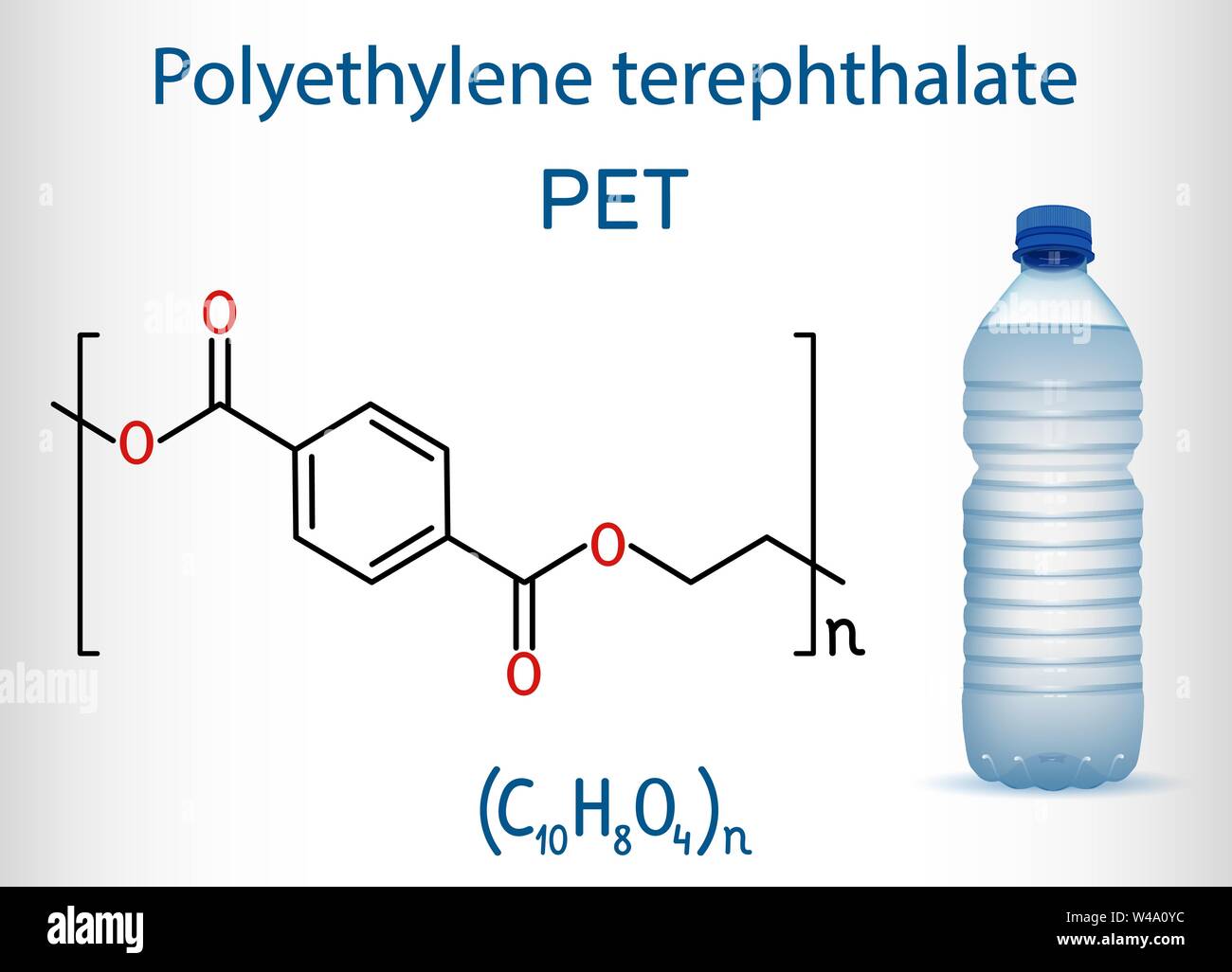
Polyethylene terephthalate or PET, PETE polyester, thermoplastic
Plastic Polymer Chemistry define key terms used in polymer chemistry. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: define key terms used in polymer chemistry. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping.
From www.slideshare.net
polymers and plastics field Plastic Polymer Chemistry In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: define key terms used in polymer chemistry. plastics. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.shalom-education.com
Polymers GCSE Chemistry Revision Plastic Polymer Chemistry A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.tes.com
Polymers and Plastics GCSE Chemistry Teaching Resources Plastic Polymer Chemistry A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. Plastic can be. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.livescience.com
What Is a Polymer? Live Science Plastic Polymer Chemistry plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. define key terms used in polymer chemistry. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.britannica.com
Polymer Description, Examples, Types, Material, Uses, & Facts Plastic Polymer Chemistry in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: define. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.thoughtco.com
Introduction to Monomers and Polymers in Chemistry Plastic Polymer Chemistry Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. in this article a brief review of the essential properties. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.alamy.com
Polyethylene terephthalate or PET, PETE polyester, thermoplastic Plastic Polymer Chemistry Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: define key terms used in polymer chemistry. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Toward Microbial Recycling and Upcycling of Plastics Plastic Polymer Chemistry Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.alamy.com
Polycarbonate (PC) plastic, chemical structure. Made from phosgene and Plastic Polymer Chemistry A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.sliderbase.com
Polymers Presentation Chemistry Plastic Polymer Chemistry plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. define key terms used in polymer chemistry. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. Plastic can be found in everything from. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.dreamstime.com
Nylon 66 or Nylon Molecule. it is Plastic Polymer Stock Vector Plastic Polymer Chemistry A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: Plastic can. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT POLYMERS “Plastics” PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Plastic Polymer Chemistry plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The Chemistry of Plastics Its Formation, Properties Plastic Polymer Chemistry Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From pixabay.com
Download Molecules, Polymer, Plastics. RoyaltyFree Stock Illustration Plastic Polymer Chemistry in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. define key terms used in polymer chemistry. a common. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT POLYMERS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID146734 Plastic Polymer Chemistry Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: plastics and natural materials such as rubber or cellulose are composed of very large molecules called polymers. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.britannica.com
Chemistry of industrial polymers Britannica Plastic Polymer Chemistry In other words, while other elements might be present, plastics always include carbon. in this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful. Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: define key terms used in polymer chemistry. plastics and natural materials such as rubber. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From www.geeksforgeeks.org
Polymers Definition, Types, Structure, Properties, and FAQs Plastic Polymer Chemistry Introduction to polymer chemistry polymer: A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. In other words, while other elements. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.
From paulmurphyplastics.com
Understanding Plastics and Polymers The Different Types of Plastic Plastic Polymer Chemistry a common name for many synthetic polymer materials is plastic, which comes from the greek word plastikos, suitable for molding or shaping. Plastic can be found in everything from airplanes to water bottles and a number. plastic is any synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymer. A large molecule (macromolecule) built up by repetitive bonding (covalent) of smaller. In other. Plastic Polymer Chemistry.